Data Protection Regulation
What Is the General Data Protection Regulation and What Does It Mean for Your Business?
The way we interact and carry out daily duties has undergone a significant transformation thanks to the internet. We submit our personal information while sending emails, sharing documents, paying bills, and making purchases online, all without giving it a second thought. Ever wonder how much of your personal information you’ve shared online? Or how about this knowledge? We’re talking about information that is saved digitally, such as bank account information, contacts, addresses, and postings on social media. This is where data protection regulation comes in.
Companies claim they gather this data so they can better serve you, communicate with you in a more relevant and targeted way, and provide you a better overall customer experience. However, do they actually use the data for this? The General Data Protection Regulation, a new European data protection regulation, was put into effect in May 2018 and permanently altered how businesses gather, keep, and utilise consumer data. This is the topic the EU has been pondering and seeking answers to.
Over half of businesses are unaware of the General Data Protection Regulation, according to a poll of more than 800 IT and business experts in charge of data protection in businesses with European clients. Only 20% of firms feel they are already GDPR compliant, according to a recent TrustArc study. What’s worst? More than two years after the May 25th deadline, 27% of businesses have yet to begin bringing their operation into conformity with the General Data Protection Regulation.
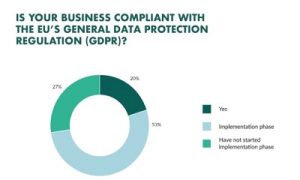
It is understandable why it has been challenging for a small brick and mortar business to prepare for General Data Protection Regulation, but according to data from the Ponemon Institute, 60% of internet businesses were also unprepared. So the General Data Protection Regulation isn’t simply being neglected by little “non-tech” businesses! We will explain what General Data Protection Regulation is, how it affects your organisation, and give helpful tips on how to guarantee General Data Protection Regulation compliance, whether you work in IT, travel, retail, or as an entrepreneur.
What is General Data Protection Regulation?
The new European privacy rule went into force on May 25, 2018.
GDPR stands for the General Data Protection Regulation.
All local privacy laws in the whole EU and EEA region have been updated to reflect this policy. It will be applicable to all businesses, even those based on other continents, who sell to or store personal data on individuals in Europe.
The EU and EEA people now have more control over their personal data thanks to the General Data Protection Regulation, which also ensures that their data is safely secured throughout Europe.
Any information relating to an individual, as defined by the General Data Protection Regulation, is deemed to be personal data. Examples include a person’s name, photograph, email address, banking information, updates to social networking sites, location data, medical information, or computer’s IP address.
People’s personal information is the same whether they are acting in their private, public, or professional capacity. People engaging and exchanging information with one another is another important aspect of the B2B ecosystem. Businesses are obviously the target audience for B2B marketing, but the connections that create difficulties for businesses are between people or individuals.
Note: Despite similarities, the General Data Protection Regulation and the new Federal Act on Data Protection in Switzerland are not the same (FADP).
The 8 basic rights of General Data Protection Regulation
Natural persons are granted the following rights under the General Data Protection Regulation:
- Right of access, which enables people to obtain information about how their personal data is being used by the firm once it has been acquired. Upon request, the business will give you a free electronic copy of your personal information.
- The right to be forgotten: Consumers have the right to have their personal data destroyed if they stop being customers or revoke their consent for a corporation to use their data.
- The right to data portability: People are entitled to move their data to another service provider. A standard, machine-readable format is also required.
- The right to information includes the requirement that people be notified prior to any data acquisition by businesses. Consumer consent must be freely granted and cannot be assumed. Consumers must choose to have their data gathered.
- The right to information rectification: This guarantees that people can amend their information if it is inaccurate, out-of-date, or incomplete.
- The right to restrict processing: People have the option to ask that their data not be processed. However, your record will no longer be used.
- The right to object: This allows people to avoid having their data processed for direct marketing purposes. No processing may continue after receiving the request; there are no exemptions. Moreover, individuals must be made aware of this immediately at the outset of any contact.
- The Right to Notification: If a data breach has occurred that exposes a person’s personal details, that person has the right to receive notification within 72 hours of learning about the breach.
The General Data Protection Regulation is the EU’s strategy for providing people greater control over their data and less control to the businesses who gather and exploit it for financial advantage.
The Business Implications of General Data Protection Regulation
Businesses and organisations are responsible for adhering to this new data protection regulation, which puts the customer in control. You are not complying if not.
What falls under General Data Protection Regulation compliance?
Well, regardless of whether data processing occurs in the EU or not, the General Data Protection Regulation is applicable to all businesses and organisations located in the EU. The General Data Protection Regulation also applies to businesses with locations outside of the EU. The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) applies to your organisation if it sells products and/or services to EU people. A data protection officer or data controller must be appointed by any business or organisation that handles personal data, and they are in charge of ensuring that the General Data Protection Regulation is followed. The General Data Protection Regulation imposes stiff fines of up to 4% of worldwide annual revenue or 20 million euros, whichever is larger, on businesses and organisations that violate it.
How serious is the EU taking General Data Protection Regulation?
Extremely Seriously.
For instance, Marriott International and British Airways both risk paying hefty fines of hundreds of millions of dollars or euros for breaking the law.
Marriott International is anticipated to be fined €99 million in the area for a data breach between 2014 and 2018. British Airways faces fines of up to €200 million for a data breach in September 2018.
Now, a lot of people would believe that Data protection regulation is only an IT problem, but that couldn’t be further from the reality. It has broad ramifications for the whole industry, including how businesses manage marketing and sales initiatives.
The Impact of General Data Protection Regulation on Customer Engagement
The General Data Protection Regulation’s standards for getting consent are harsher because the individual must have the ability to revoke consent at any time and because consent that does not include distinct consents is deemed invalid for various processing activities. This implies that you must be able to demonstrate that the individual has given their agreement to a certain action, like receiving a newsletter. It is not acceptable to accept or include a disclaimer, and having an opt-out is not adequate.
Many things for businesses have changed as a result of the General Data Protection Regulation, including how their sales teams acquire customers and how marketing initiatives are managed. To comply with double opt-in regulations and email marketing best practises, organisations have had to redesign business procedures, applications, and forms. Prospects must complete a form or check a box to opt-in to communication, and they must then confirm their actions in a second email.

If a person chooses not to receive the message, organisations must show that consent has been provided. This calls for the inclusion of a time-stamped audit trail and reporting details indicating what the contact opted into and how in all kept data. Even if a vendor or outsourced partner was in charge of data collection, you are still in charge of acquiring the proper permission information if you acquire marketing lists. At a trade fair, salespeople in the B2B sector meet new clients, exchange business cards, and afterwards add the connections to the company’s mailing list. This is not feasible in 2020. Businesses must come up with innovative methods for gathering client data.
Preparations for General Data Protection Regulation -compliance
Privacy by design is a key component of the General Data Protection Regulation. All corporate divisions must carefully examine their data and the way it is handled in order to comply with privacy by design. A business must take a lot of steps to adhere to the General Data Protection Regulation. Here are a few ideas to get you moving toward compliance if you haven’t already.
- Map your company’s data
Keep track of the sources of all personal data in your business, as well as what you do with it. Determine the data’s location, its users, and whether it is at risk. Additionally to being crucial for the General Data Protection Regulation, this advances client relationship management.
- Determine what data you need to keep
Keep only the information you need, and delete any information you aren’t utilising. Consider which data is crucial to your company currently if your company has gathered a lot of data without any meaningful usefulness. The General Data Protection Regulation promotes a stricter approach to the handling of personal data.
When cleaning up, consider the following:
Ask yourself these questions as you go through the cleanup process:
- Why precisely are we preserving this data as opposed to just destroying it?
- Why are all these data being saved?
- What are we attempting to accomplish by gathering all of this personal data in these many categories?
- Is erasing this data more profitable than encrypting it from prying eyes?
- Put security measures in place
Create and apply security measures throughout your infrastructure to prevent data breaches. This entails putting security measures in place to guard against data breaches and acting quickly to alert people and the appropriate authorities should a breach occur. Unsettlingly, the legal firm EMW discovered that since the implementation of the General Data Protection Regulation, complaints regarding data breaches had grown by 160%.
Check with your suppliers as well, and be sure to. You are still responsible even if you outsource, so be sure they have the proper security measures in place. Consider the most recent data hack that affected businesses utilising Typeform, a third-party survey service. The data breach was quickly disclosed by Typeform, who also provided a template for their clients that utilised their programme to gather personal data (as shown below).

- Review your documentation
Individuals must expressly consent to the collection and processing of personal data in accordance with the General Data Protection Regulation. Pre-checked boxes and implied consent won’t be taken into account anymore. You must go through each of your privacy declarations and statements, and make any required adjustments.
- Establish procedures for handling personal data
Individuals under the General Data Protection Regulation have eight fundamental rights, as was previously indicated.
Now that you know how you will respond to each of these scenarios, you need to set rules and procedures.
For instance:
- How do people legally grant their consent?
- How does a person go about having their data deleted?
- What steps will you take to guarantee that the information is removed across all platforms?
- How will you send a person’s data if they request it?
- How will you verify that the individual requesting the transfer of his data is who he claims to be?
- In the event of a data breach, what is the notification strategy?
Conclusion
In this new environment, data is a valuable form of currency. Additionally, the General Data Protection Regulation presents possibilities as well as obstacles for our business. Companies that demonstrate a greater respect for consumer privacy (beyond merely complying with regulations), are open about how data is used, and create and adopt new and better methods of handling customer data throughout its lifespan, will gain and keep more devoted customers.
It appeared like there would be plenty of time for startups to make the required preparations when it was initially announced in 2016. But even beyond the deadline, a lot of businesses are still having trouble. Therefore, if you haven’t begun your road toward compliance yet, we highly advise you to do so right away. Use the advice in this article as a starting point as you take the time to comprehend what you must do to remain compliant. So that you and your company can make a complaint as quickly as feasible, prepare an action plan for your General Data Protection Regulation roadmap.
About the Author
Ahsan Azam is the author who specializes in avionics as well as research writing. The author has a keen attention to detail and is focused on providing interesting content to the readers.
About Stone Age Technologies SIA
Stone Age Technologies SIA is a reliable IT service provider, specializing in the IT Solutions. We offer a full range of services to suit your needs and budget, including IT support, IT consultancy, remote staffing services, web and software development as well as IT outsourcing. Our team of highly trained professionals assist businesses in delivering the best in IT Solutions. Contact us for your IT needs. We are at your service 24/7.









Write a Comment